Evolutionary biochemistry: revealing the historical and physical causes of protein properties | Nature Reviews Genetics
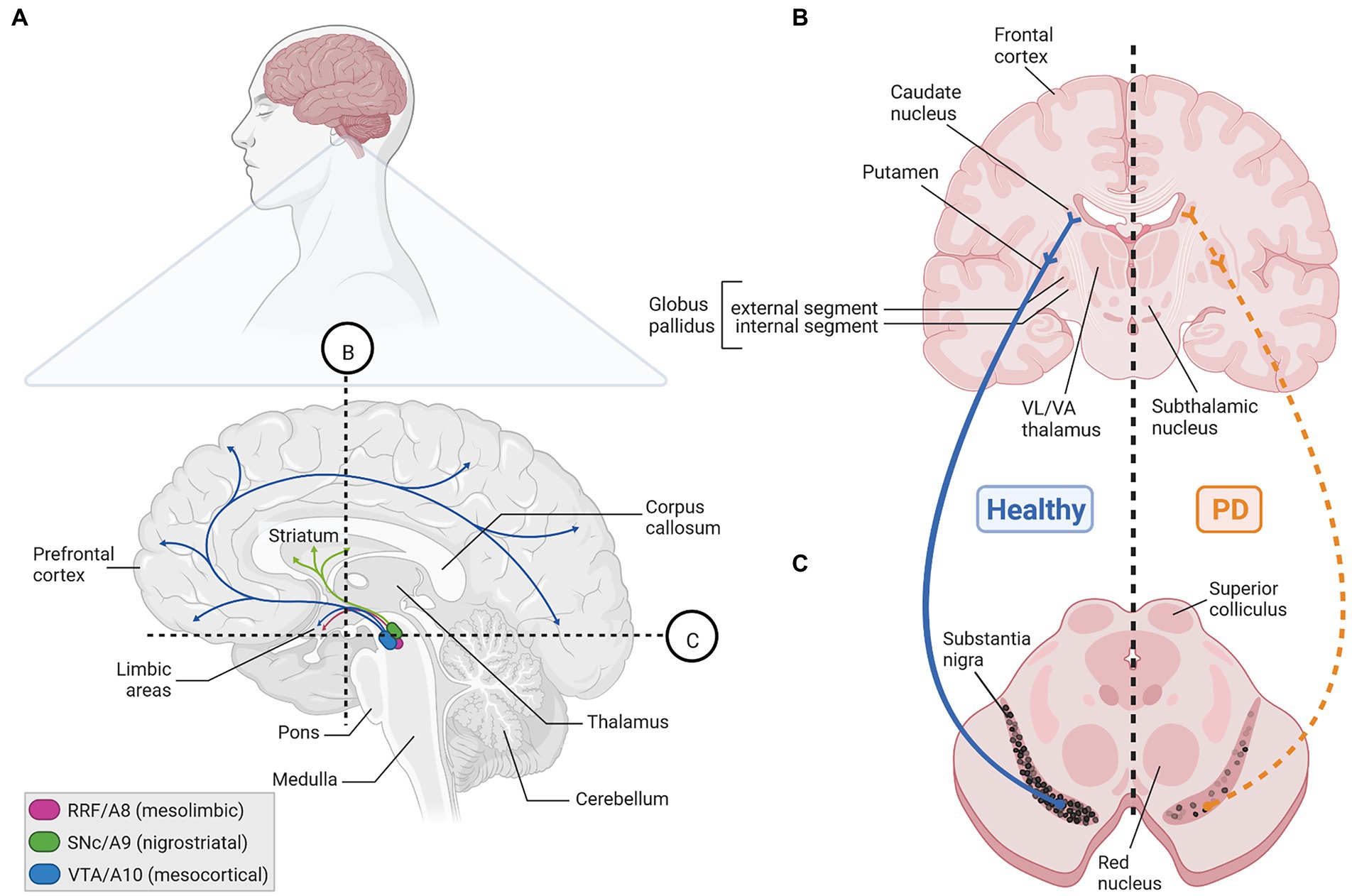
Frontiers | Developmental pathways linked to the vulnerability of adult midbrain dopaminergic neurons to neurodegeneration
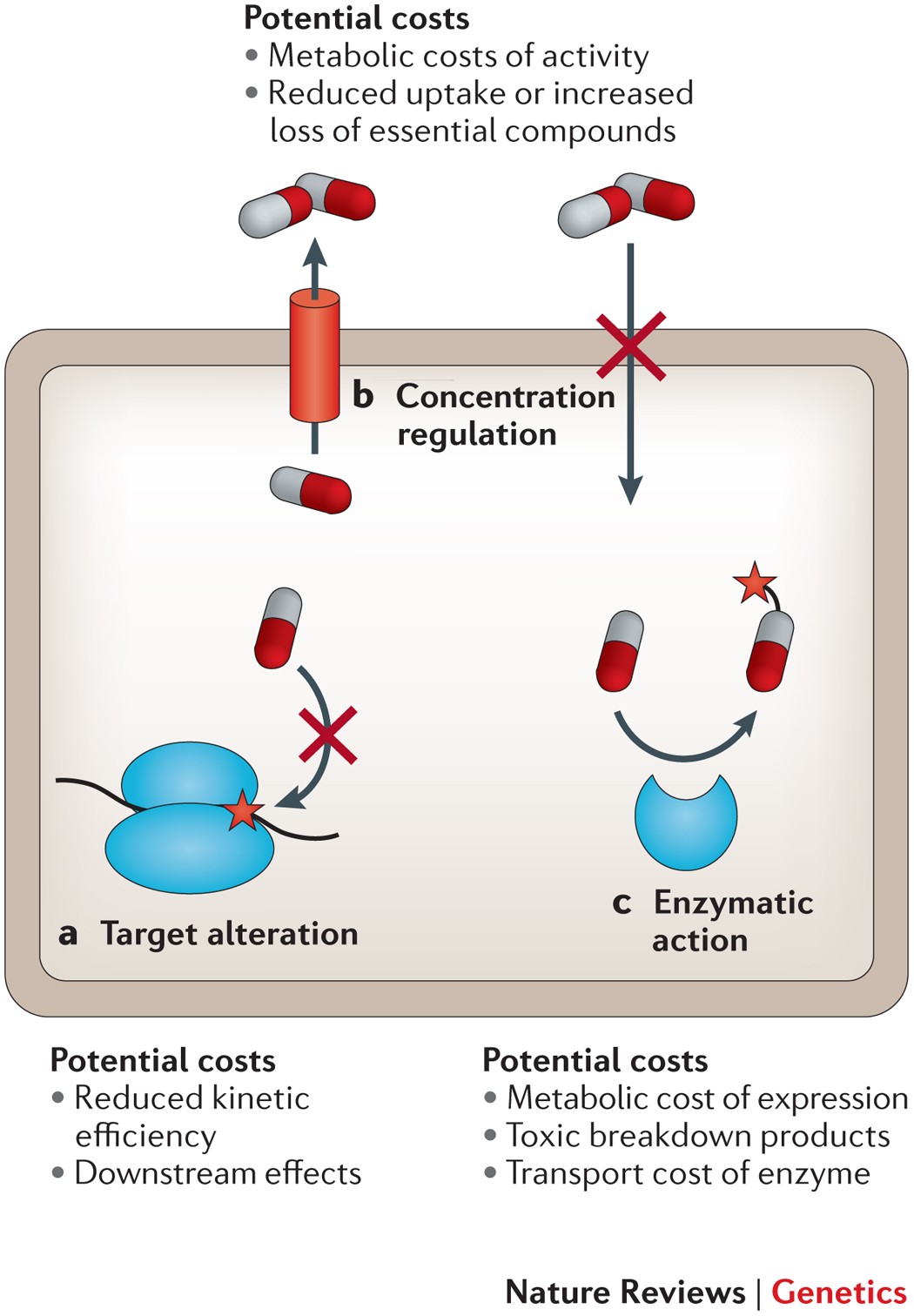
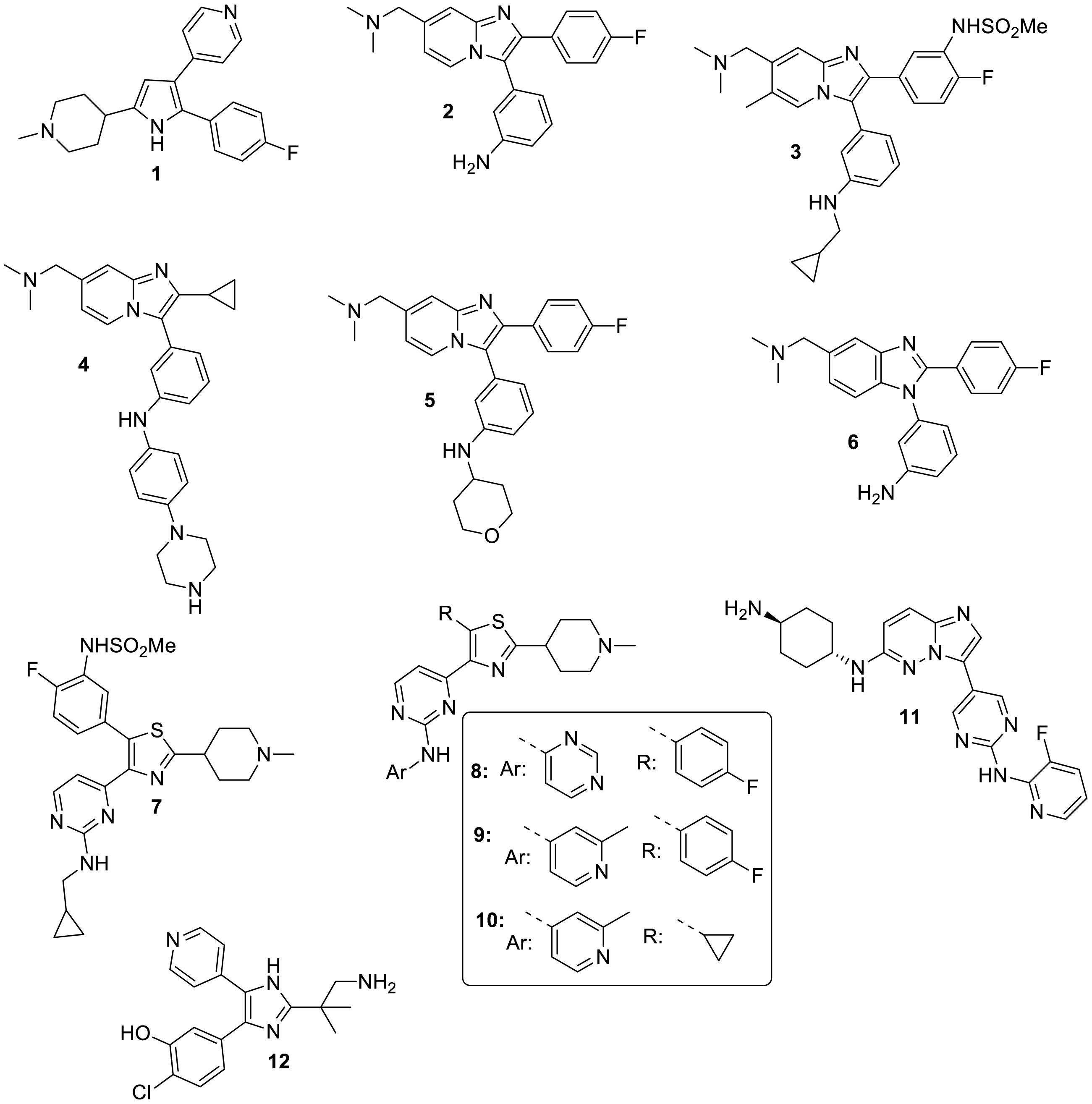
Evolutionary consequences of drug resistance: shared principles across diverse targets and organisms | Nature Reviews Genetics
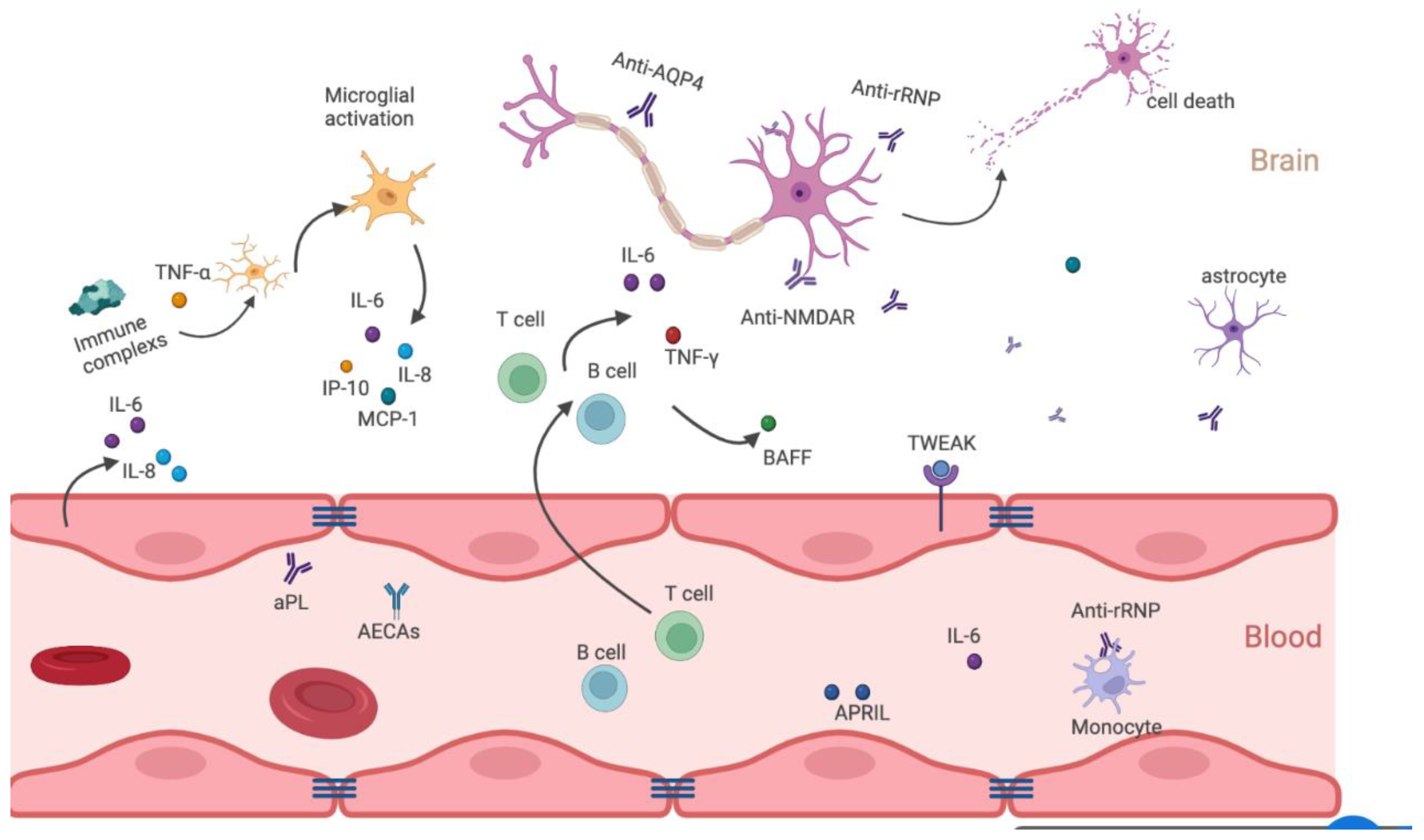
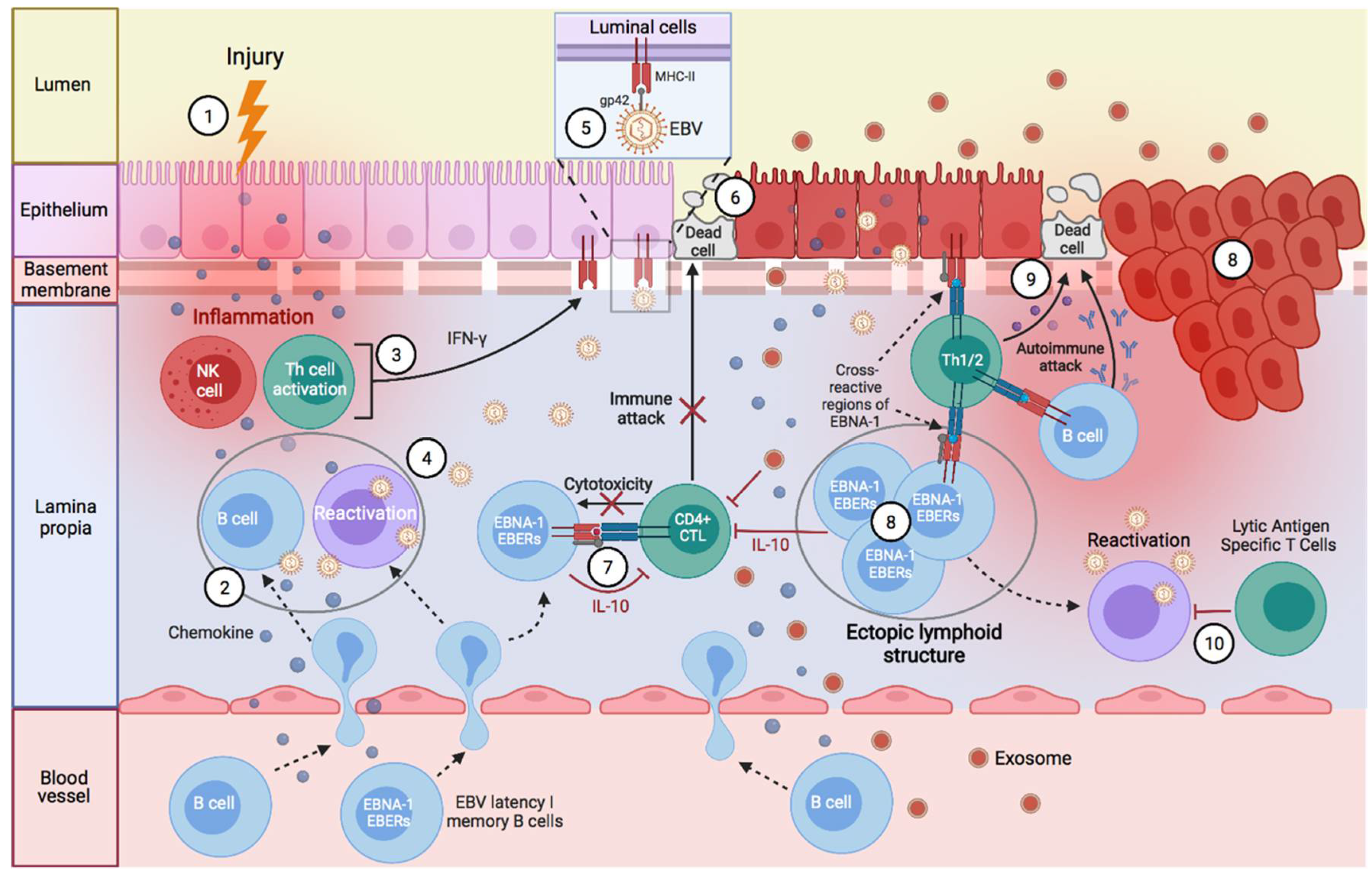
JCM | Free Full-Text | Progress in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus

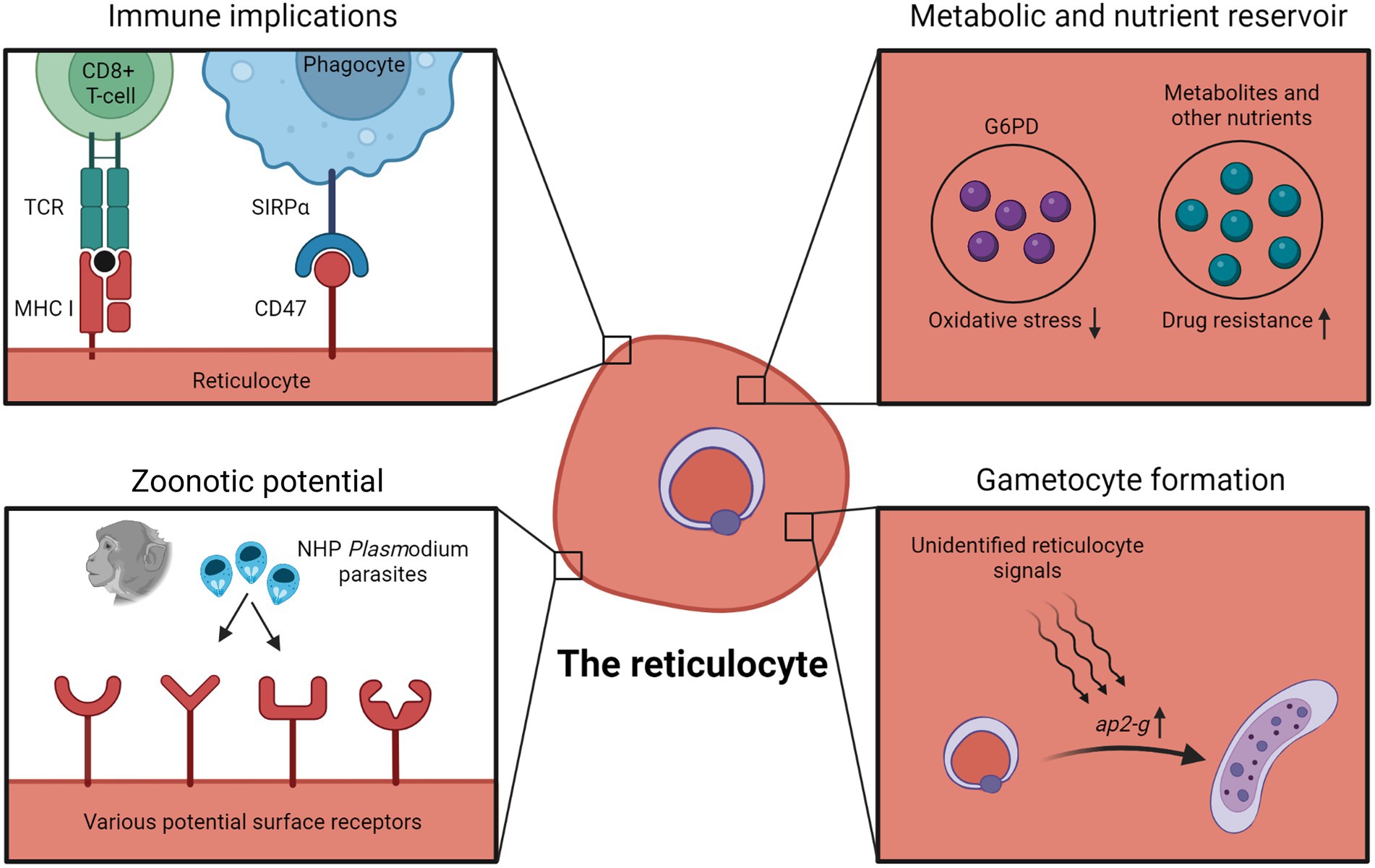
Nutrient Limitation Magnifies Fitness Costs of Antimalarial Drug Resistance Mutations | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy

Nutrient Limitation Magnifies Fitness Costs of Antimalarial Drug Resistance Mutations | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy

Whole-Cell Phenotypic Screening of Medicines for Malaria Venture Pathogen Box Identifies Specific Inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum Late-Stage Development and Egress | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy

Nutrient Limitation Magnifies Fitness Costs of Antimalarial Drug Resistance Mutations | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
Full article: Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: Understanding of clinical features, genetic basis, and pathobiology of disease guides therapeutic strategies

A Platform of Regioselective Methodologies to Access Polysubstituted 2‐Methyl‐1,4‐naphthoquinone Derivatives: Scope and Limitations - Rodo - 2016 - European Journal of Organic Chemistry - Wiley Online Library